2025-03-07
GECC public chain "GECC Carbon Assets" blockchain technology has ushered in a major breakthrough!
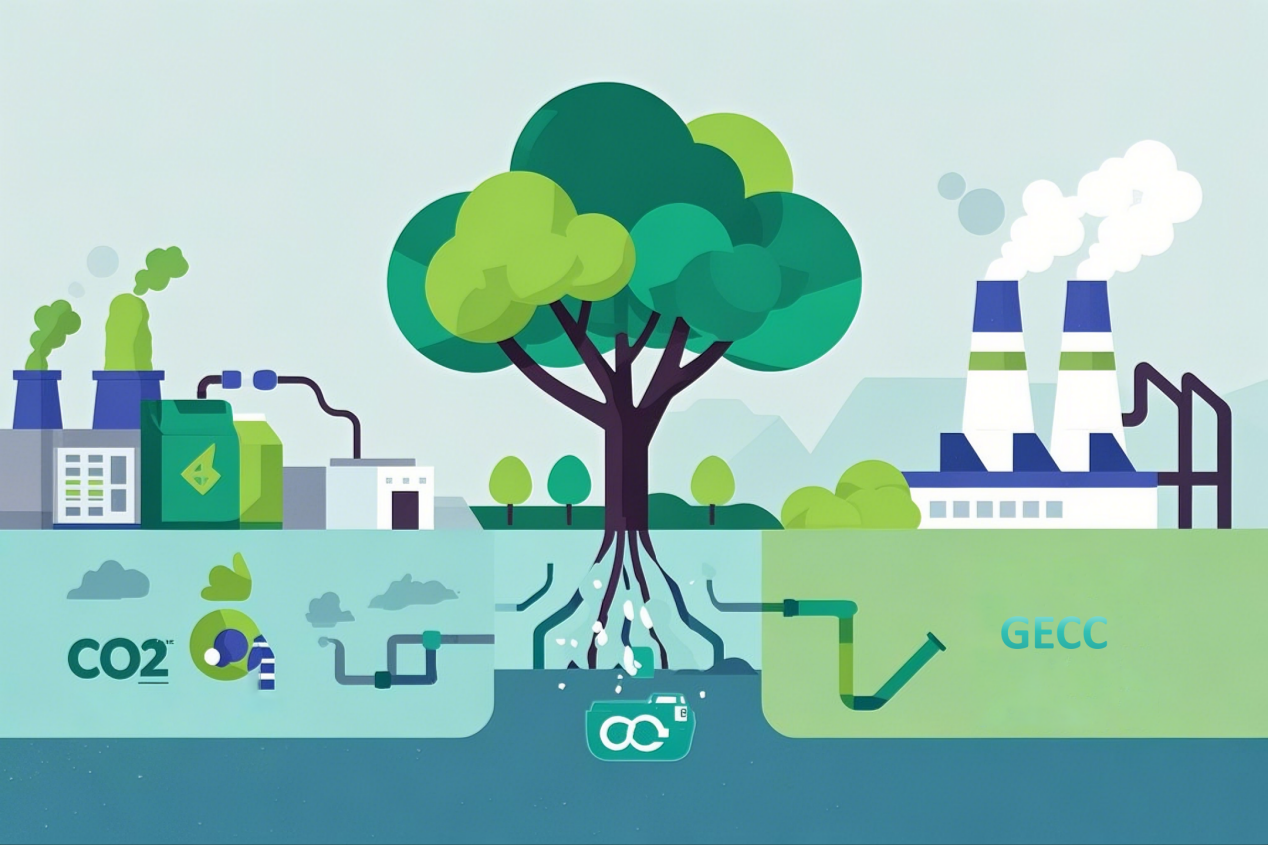
According to the latest news from the R3 blockchain alliance, the GECC public chain has made major breakthroughs in technologies such as "carbon reduction, carbon storage, carbon capture, and carbon utilization," and introduced blockchain technology in the process to improve carbon sink capabilities, so that ordinary users can create income through carbon neutrality and carbon asset transactions in the system, thereby encouraging more people to participate and implement the goal of carbon neutrality. Specifically, partners are rewarded by participating in carbon emission products, wind power projects, carbon neutral electricity, and other processes.
In the GECC public chain system, users can save carbon emissions in their daily lives, which will be calculated as "GECC carbon assets" to cultivate and encourage more people to participate in low-carbon and environmentally friendly behaviors. While supporting the construction of the GECC carbon sink ecosystem, people also participate in green environmental protection, improve the user group's awareness of low-carbon protection, and accelerate the arrival of the carbon neutral era. By continuously accumulating carbon assets, participants (institutional partners, ordinary users, etc.) can receive continuous rewards.
GECC public chain's "diversified application scenarios" help "low-carbon emission reduction"!
Faced with a complex ecological system, carbon neutrality data records and carbon asset transactions have limited self-exploration power in the market. It is necessary to find a more efficient construction and operation model to promote the orderly organization of ecological stakeholders and establish a collaborative operation system, so as to achieve the true integration of blockchain and industry. To this end, the GECC public chain system conducts top-level architecture design from the following three aspects. First, extract the commonalities between carbon neutrality data records and carbon asset trading fields and related industries; second, support the customizability and scalability of the industry without affecting the innovation of the industry; third, promote collaboration and sharing between different industries and break through the bottleneck of single application.
GECC carbon assets, like a magic key, open the door to the carbon emission rights trading market. It is a tradable right or certificate closely linked to greenhouse gas emission reduction. If an enterprise or organization can effectively reduce carbon emissions or enhance carbon sink capacity through technological innovation, energy conservation and emission reduction, it can harvest precious carbon assets such as carbon emission rights and emission reduction credits (such as CCER), and then trade them in the market.
This mechanism cleverly links environmental protection with economic interests, motivating enterprises and society to forge ahead on the path of emission reduction.
At the same time, the carbon emission allowance (CEA) is set by the government, which sets a clear limit for the carbon emissions of enterprises. Just like the speed limit signs in traffic rules, if an enterprise exceeds the emission limit, it needs to purchase quotas to make up for the excess emissions; on the contrary, if it is below the limit, it can sell excess quotas and reap economic rewards. This measure encourages enterprises to be thrifty, strive to optimize production processes and reduce carbon emissions.
Therefore, the first step in building the GECC public chain system is to determine the user subject and user needs, that is, to explore the problems between the user subject and other factors in carbon neutrality data records and carbon asset transactions in the user domain, and propose improvement needs. Among them, the correlation between multiple user subjects and the demand boundary are the entrances to determine the application ecology of carbon neutrality data records and carbon asset transactions. For complex systems, the demand iteration model can be adopted to gradually advance.

Finally, the particularity of carbon neutrality data recording and carbon asset trading in the GECC public chain system requires that it must be combined with the Internet of Things. The integration of the system and the Internet of Things includes the integration of architecture and stakeholders. The architectural integration fully integrates the Internet of Things model and the functional architecture of the GECC system blockchain to integrate the technical characteristics of the GECC system such as trust and consensus into the Internet of Things environment, solving the problems of single-point network failures and complex technical industrial chains faced by the Internet of Things under the application ecology of carbon neutrality data recording and carbon asset trading. The integration of stakeholders regards the relevant elements in the Internet of Things model as service customers of the blockchain, and promotes the establishment of a collaborative system, a trust system and a value system among all stakeholders in the Internet of Things. The addition of the Internet of Things will make future carbon neutrality data recording and carbon asset trading more intelligent.

Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other media. The purpose of reprinting is to convey more information. It does not mean that this website agrees with its views and is responsible for its authenticity, and does not bear any legal responsibility. All resources on this site are collected on the Internet. The purpose of sharing is for everyone's learning and reference only. If there is copyright or intellectual property infringement, please leave us a message.
©copyright 2009-2020 Zao Bao Daily Contact Us SiteMap